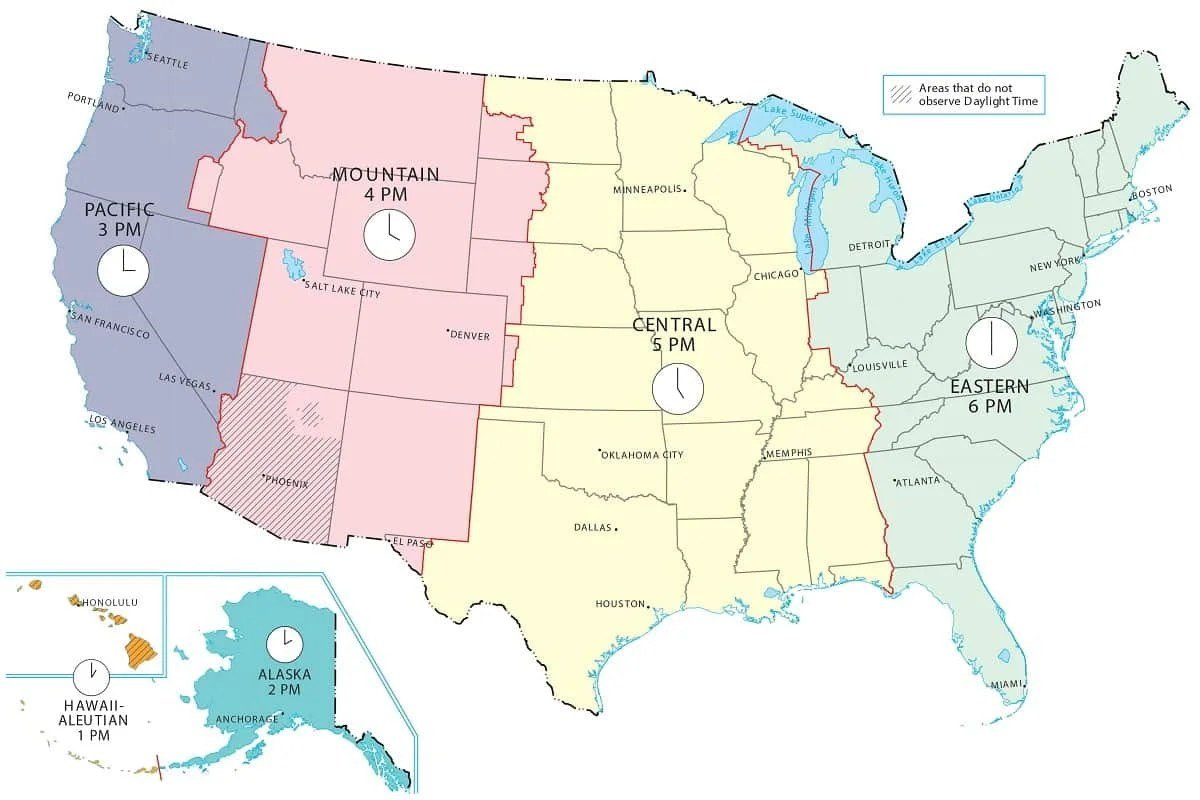
When you're trying to sync schedules across continents, book a flight, or just figure out when your favorite show airs, time zones aren't just an abstract concept — they're a daily reality. Among the most impactful for North Americans and those interacting with the region is the Central Time Zone (CT). More than just a line on a map, understanding the Central Time Zone (CT) and its scope is crucial for seamless coordination, preventing missed connections, and staying connected in a rapidly globalizing world. It’s a vast geographical swath, influencing millions of lives and countless transactions every single day.
Let's demystify it together.
At a Glance: Key Takeaways for Central Time
- Primary North American Zone: CT is a major time zone in North America, sitting one hour behind the Eastern Time Zone (ET).
- Two Faces of CT: It switches between Central Standard Time (CST) at UTC-6 during colder months and Central Daylight Time (CDT) at UTC-5 during warmer months.
- DST Dynamics: Most regions observing CT advance their clocks for Daylight Saving Time (DST) from March to November.
- Global Reach: CT covers parts of Canada, the United States, Mexico, and much of Central America, impacting international business and communication.
- Major Hubs: Iconic cities like Chicago, Dallas, Houston, Mexico City, and Nashville operate on Central Time.
- Key Exceptions: Not all areas in the Central Time Zone observe DST; notably, most of Saskatchewan, Canada, and the majority of Mexico stick to CST (UTC-6) year-round.
The Pulse of the Continent: What Exactly is Central Time?
Imagine a vast stretch of North America, from the icy plains of Canada down through the heartland of the U.S., into the bustling metropolises of Mexico, and wrapping around the tropical nations of Central America. This enormous area largely operates under the umbrella of Central Time.
At its core, Central Time is one hour behind the Eastern Time Zone (ET) and one hour ahead of the Mountain Time Zone (MT). This seemingly simple offset, however, carries significant weight due to the sheer size and economic power of the regions it encompasses.
But Central Time isn't always just one time. It has two primary variations that shift with the seasons:
- Central Standard Time (CST): This is the baseline, observed during the fall and winter months. Internationally, it's designated as UTC-6, meaning it's six hours behind Coordinated Universal Time.
- Central Daylight Time (CDT): As the days lengthen and temperatures rise, many areas observing CT switch to CDT. This "spring forward" moves the clock one hour ahead, making it UTC-5, or five hours behind Coordinated Universal Time.
Understanding this distinction between CST and CDT is paramount, especially when coordinating across time zones, as a simple "CT" reference could be ambiguous depending on the time of year.
The Great Clock Shift: Navigating Daylight Saving Time (DST) in Central Time
The twice-yearly ritual of Daylight Saving Time can feel like a minor headache, but it’s a critical component of how most of the Central Time Zone functions. The idea, primarily, is to make better use of daylight hours during warmer months, shifting an hour of evening light to the morning.
For regions observing DST within CT, here’s how it typically works:
- Spring Forward: Clocks jump forward one hour from CST (UTC-6) to CDT (UTC-5). This usually occurs at 2:00 AM on the second Sunday in March, instantly becoming 3:00 AM CDT.
- Fall Back: Clocks move back one hour from CDT (UTC-5) to CST (UTC-6). This happens at 2:00 AM on the first Sunday in November, reverting to 1:00 AM CST.
These shifts impact everything from meeting schedules to travel itineraries. Always double-check if a specific date falls within CDT or CST if you're dealing with a region that observes DST.
When Central Time Defies DST: Notable Exceptions
While the majority of the Central Time Zone in the U.S. and parts of Canada observe DST, there are significant exceptions that you absolutely need to be aware of:
- Saskatchewan, Canada: Most of this Canadian province observes CST year-round, meaning it does not switch to CDT. This makes it effectively on the same time as Mountain Daylight Time during summer months. A quirky exception within Saskatchewan is the city of Lloydminster, which observes Mountain Time with DST, creating a unique local dynamic.
- Mexico: In a major shift, Mexico abolished Daylight Saving Time in October 2022. This means the vast majority of Mexican regions that fall within the Central Time Zone (known as Zona Centro) now observe CST (UTC-6) year-round. This simplification removes a layer of complexity for those interacting with Mexico but also means you can no longer assume a DST switch.
- Central American Nations: Countries like Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua consistently use Central Standard Time (UTC-6) year-round, never adjusting for DST. Panama, while geographically proximate, uses Eastern Standard Time (UTC-5) year-round.
These exceptions highlight why a diligent check of local time rules is always a good practice, rather than making broad assumptions.
Mapping the Central Time Zone: A Geographic Tapestry
The Central Time Zone carves a wide path across North America, connecting diverse landscapes and vibrant communities. Its geographical coverage is extensive, making it a critical hub for commerce, culture, and communication.
Let's break down its presence across different countries:
Canada's Central Slice
In Canada, Central Time primarily dominates the heart of the country:
- Manitoba: The entire province of Manitoba observes Central Time, shifting between CST and CDT. Winnipeg, its capital, is a major CT city.
- Nunavut: Western areas of this vast territory also follow Central Time.
- Ontario: A small, northwestern portion of Ontario, particularly around the city of Kenora, is on Central Time.
- Saskatchewan: As mentioned, most of Saskatchewan uses CST year-round.
The United States' Heartland
The U.S. demonstrates the Central Time Zone's vastness, with many states entirely within it and others split between time zones.
States Entirely within Central Time:
These ten states reside fully in the Central Time Zone, observing DST as applicable:
- Alabama
- Arkansas
- Illinois
- Iowa
- Louisiana
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Oklahoma
- Wisconsin
States Split Between Central and Mountain Time:
Five states navigate a split, creating internal time zone boundaries: - Kansas
- Nebraska
- North Dakota
- South Dakota
- Texas
For example, most of Texas is in CT, but its westernmost county, El Paso, operates on Mountain Time. To know the current time in Dallas Fort Worth, for instance, you'd look to the Central Time Zone, specifically CDT or CST depending on the season.
States Split Between Central and Eastern Time:
Another five states straddle the line between Central and Eastern Time, often along county borders: - Florida (Panhandle often CT)
- Indiana (some western counties CT)
- Kentucky (western counties CT)
- Michigan (some western Upper Peninsula counties CT)
- Tennessee (western third CT)
These split states require careful attention when planning travel or communications to ensure you're on the right local time.
Mexico's Zona Centro
Mexico's time zone landscape was significantly simplified after abolishing DST. Most of the country, roughly the eastern three-fourths, falls into the Central Time Zone, locally known as Zona Centro. This includes:
- Mexico City, the bustling capital
- Many other federal entities and major cities
Crucially, these regions now observe CST (UTC-6) year-round. Exceptions include five northwestern states and the southeastern state of Quintana Roo, which uses Eastern Standard Time (UTC-5) year-round without DST.
Central America's Consistent Clock
Many Central American nations consistently operate on Central Standard Time (UTC-6) year-round, never adjusting for DST. This simplifies coordination with them:
- Belize
- Costa Rica
- El Salvador
- Guatemala
- Honduras
- Nicaragua
Remember, Panama is an outlier in this region, observing Eastern Standard Time (UTC-5) year-round.
Navigating the Global Clock: CT's Far-Reaching Influence
The Central Time Zone isn't just a regional marker; its global implications are profound. With major economic hubs like Chicago and Mexico City, CT plays a significant role in international affairs, influencing decisions and operations across continents.
- International Business & Finance: For companies with offices or clients in CT, coordination with European, Asian, and other North American markets is a daily exercise. Financial markets, supply chains, and legal deadlines all hinge on accurate time zone conversions.
- Travel and Logistics: Planning international flights, cargo shipments, or simply coordinating pick-ups across borders demands a keen awareness of CT, especially with its DST shifts and regional exceptions.
- Media and Broadcasting: Live events, news coverage, and syndicated programming often list times in multiple zones, with CT being a standard reference point for a large portion of the North American audience.
- Remote Work and Global Teams: As remote work becomes the norm, understanding CT is vital for scheduling team meetings, project deadlines, and ensuring effective collaboration among distributed teams. A CT-based team member might be wrapping up their day when a colleague in Tokyo is just starting theirs.
Practical Time Conversion Examples
To illustrate the global impact, let's look at some common conversions from Central Time (assuming CDT for summer and CST for winter, if not specified, but for these examples, we'll use the precise UTC offset):
| Central Time (CST/UTC-6) | Central Time (CDT/UTC-5) | Eastern Time (ET) | Greenwich Mean Time (GMT/UTC) | Central European Time (CET/UTC+1) | Japan Standard Time (JST/UTC+9) | Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST/UTC+10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 08:00 AM CST | 09:00 AM ET | 02:00 PM GMT | 03:00 PM CET | 11:00 PM JST | 12:00 AM AEST (next day) | |
| 08:00 AM CDT | 09:00 AM ET | 01:00 PM GMT | 02:00 PM CET | 10:00 PM JST | 11:00 PM AEST (same day) | |
| 12:00 PM CST | 01:00 PM ET | 06:00 PM GMT | 07:00 PM CET | 03:00 AM JST (next day) | 04:00 AM AEST (next day) | |
| 12:00 PM CDT | 01:00 PM ET | 05:00 PM GMT | 06:00 PM CET | 02:00 AM JST (next day) | 03:00 AM AEST (next day) | |
| 06:00 PM CST | 07:00 PM ET | 12:00 AM GMT (next day) | 01:00 AM CET (next day) | 09:00 AM JST (next day) | 10:00 AM AEST (next day) | |
| 06:00 PM CDT | 07:00 PM ET | 11:00 PM GMT | 12:00 AM CET (next day) | 08:00 AM JST (next day) | 09:00 AM AEST (next day) | |
| This table showcases the constant juggling act required for global coordination, emphasizing the critical difference between CST and CDT for those interacting with areas observing DST. |
Your Toolkit for Mastering Central Time
Successfully navigating Central Time, with its DST variations and international scope, requires more than just a passing familiarity. Here are actionable insights to keep you on schedule and prevent time-related mishaps:
- Leverage Digital Tools Aggressively: Your smartphone, computer, and digital assistants are your best friends here.
- World Clock Apps: Google Clock, Apple Clock, and various third-party apps allow you to add multiple cities and time zones, giving you an instant overview.
- Scheduling Platforms: Tools like Calendly, Zoom, Google Calendar, and Outlook Calendar inherently understand time zones. Always set up meetings in your local time zone, and let the platform convert it for attendees. Crucially, encourage participants to verify their own time zone settings within these tools.
- Desktop Clocks: Many operating systems allow you to display multiple clocks on your taskbar or desktop for quick reference.
- Always Confirm Current Status (CST vs. CDT): This is perhaps the single most important rule. Before making a critical call, booking a flight, or scheduling a meeting, quickly verify whether the Central Time region you're dealing with is currently observing CST or CDT. A simple web search like "current time in Chicago" or "is Chicago on CDT or CST?" can save you from a costly error. Remember, the 'Standard' versus 'Daylight' designation changes twice a year for most.
- Plan Ahead with Global Participants in Mind: If your audience or contacts span multiple time zones, including Central Time, be explicit in your communications:
- Specify Time Zones: Instead of "Meeting at 10 AM," say "Meeting at 10 AM CT (Central Time)" or, even better, "10 AM CDT (UTC-5)." For maximum clarity, consider adding the equivalent in your own local time or popular reference zones (e.g., "10 AM CDT / 11 AM ET").
- Provide a Time Zone Converter Link: Many free online converters allow people to input a time and date and see it in their local zone.
- Consider "Overlapping Hours": When scheduling global meetings, identify periods where the most participants are likely to be awake and productive, even if it's not ideal for everyone.
- Double-Check Before Critical Events: This cannot be overstated. Before a job interview, a flight departure, a crucial client call, or a live broadcast, take a moment to reconfirm the exact local time in all relevant locations. A quick check of a reliable world clock or local news site can prevent missed opportunities or serious blunders caused by overlooking DST changes or conversion errors.
- Set Your Devices to Automatically Adjust: Most modern smartphones, computers, and smart devices have settings to automatically adjust for Daylight Saving Time. Ensure this feature is enabled for your primary location to avoid personal time confusion. However, be aware that manual overrides or travel can sometimes disrupt this, so a quick verification is still wise.
Common Central Time Questions Answered
Understanding the nuances of Central Time often brings up specific questions. Here are clear, concise answers to some frequently asked ones:
Q: Is Central Time always one hour behind Eastern Time?
A: Yes, Central Time is consistently one hour behind Eastern Time. So, if it's 3 PM ET, it's 2 PM CT. This relationship holds true whether both are on Standard Time or Daylight Saving Time, or even if one observes DST and the other doesn't (though the UTC offset would differ).
Q: Does Central Time always observe Daylight Saving Time?
A: No. While most of the Central Time Zone in the United States and parts of Canada observe DST, there are significant exceptions. Most of Saskatchewan, Canada, uses CST year-round, and the majority of Mexico (within CT) now observes CST year-round after abolishing DST in October 2022. Several Central American countries also remain on CST year-round.
Q: How do I know if it's CST or CDT?
A: Most regions observing DST switch to CDT (UTC-5) from the second Sunday in March until the first Sunday in November. During the other months, it's CST (UTC-6). If you're unsure, a quick online search for "current time in [city in CT]" will usually specify CST or CDT.
Q: Why is Mexico now on CST year-round?
A: Mexico abolished Daylight Saving Time nationwide in October 2022, citing health concerns and energy savings that were not as significant as once believed. Therefore, most regions within its Central Time Zone now permanently observe Central Standard Time (UTC-6).
Q: Which major U.S. cities are in the Central Time Zone?
A: Prominent U.S. cities in the Central Time Zone include Chicago (Illinois), Dallas (Texas), Houston (Texas), Nashville (Tennessee), New Orleans (Louisiana), St. Louis (Missouri), and Minneapolis (Minnesota).
Q: If I'm traveling from ET to CT, do I gain or lose an hour?
A: If you travel from a region observing Eastern Time to a region observing Central Time, you will gain an hour. For example, if you depart at 10:00 AM ET and arrive an hour later, your watch will show 10:00 AM CT upon arrival, effectively giving you an extra hour.
Staying in Sync: Your Continuous Time Zone Journey
Understanding the Central Time Zone isn't just about memorizing facts; it's about developing a keen awareness of its dynamic nature and applying practical strategies to navigate it effectively. Whether you're a business professional coordinating across continents, a traveler planning your itinerary, or simply someone trying to catch a remote event, the principles remain the same: verify, clarify, and utilize the tools at your disposal.
The world continues to spin, and time zones, with their shifts and exceptions, are a fundamental part of its rhythm. By mastering the ins and outs of Central Time, you're not just learning about clocks; you're gaining a valuable skill that helps you stay connected and punctual in an interconnected world. So, go forth with confidence, knowing you have the insights to conquer any Central Time challenge thrown your way.